Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient vital for DNA production, red blood cell formation, immune function, and healthy nerve operation. While the recommended daily intake is 2.4 micrograms (mcg) for adults, many people don’t get enough through diet alone. This is especially true for those following plant-based diets. Here’s a breakdown of the top 18 foods richest in this crucial vitamin, along with preparation tips and why B12 matters.
Why B12 Deficiency Matters
B12 isn’t produced by the body, so we rely on dietary intake. Deficiency can lead to fatigue, neurological issues, and even irreversible nerve damage. The risk increases with age, certain medical conditions, and vegan/vegetarian lifestyles, as B12 is primarily found in animal products.
Top B12-Rich Foods
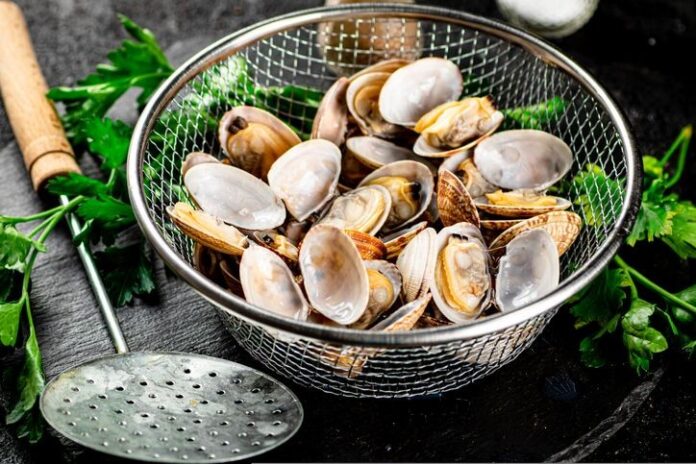
- Clams (84.1 mcg / 3oz): These shellfish deliver an astounding 3,504% of your daily B12 needs. Enjoy them steamed, boiled, or in soups.
- Purple Layer Seaweed (30-60 mcg / 100g): Packed with iodine and B12, this seaweed adds umami flavor to pasta or snacks.
- Oysters (24.5 mcg / 3oz): Beyond B12, oysters are a zinc powerhouse, boosting immunity and wound healing. Serve chilled as an appetizer.
- Nutritional Yeast (24 mcg / 3 tbsp): A vegan staple, this cheesy seasoning provides protein and other B vitamins. Sprinkle it on popcorn or pasta.
- Mussels (20.4 mcg / 3oz): Similar to clams, mussels offer protein, potassium, and omega-3s. Prepare them the same way: steam or boil until shells open.
- Crab (7.6 mcg / 3oz): Rich in vitamins A, B, and C, crab also delivers a hefty dose of zinc. Use it in cakes, chowders, or salads.
- Sardines (7.6 mcg / 3oz): These small fish are loaded with calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3s. Pair them with spaghetti squash for a tasty meal.
- Trout (5.4 mcg / 3oz): Fatty fish like trout are excellent sources of vitamin D and omega-3s, promoting brain health and reducing inflammation.
- Salmon (3.8 mcg / 3oz): A protein-packed choice with heart-healthy omega-3s. Bake or grill instead of frying for maximum benefits.
- Tuna (1.8 mcg / 3oz): Canned tuna offers vitamin D and omega-3s, but choose light tuna in water for healthier options.
- Haddock (1.8 mcg / 3oz): A lean protein source with flaky texture. Bake it with lemon and herbs for a simple yet delicious meal.
- Beef (1.6 mcg / 3oz): Lean cuts provide zinc, protein, and riboflavin, which may ease PMS symptoms.
- Milk (1.5 mcg / 1 cup): A convenient source of calcium, vitamin D, and potassium. Blend it into smoothies for added nutrition.
- Greek Yogurt (1 mcg / 7oz): Packed with calcium, probiotics, and protein, opt for non-fat or low-fat varieties.
- Fortified Breakfast Cereal (0.6 mcg / serving): A helpful option for vegans and vegetarians, but choose whole-grain cereals for fiber.
- Eggs (0.6 mcg / large egg): A versatile source of protein and vitamin D. Enjoy them boiled, scrambled, or in omelets.
- Chicken Breast (0.4 mcg / 1 cup): Lean protein with less saturated fat than red meat. Grill, roast, or bake for a healthy meal.
- Turkey (0.3 mcg / 3oz): A serving provides nearly half your recommended selenium intake, boosting immune function.
Supplements and Special Diets
Vitamin B12 supplements are available in B-complex formulas, multivitamins, or standalone doses. Consult a healthcare provider before taking supplements, as they may interact with medications. Vegetarians and vegans should prioritize fortified foods or consider supplements to avoid deficiency.
In conclusion, ensuring adequate B12 intake is crucial for overall health. By including these foods in your diet or considering supplementation, you can maintain optimal neurological function, energy levels, and immune strength.